Brick & Mortar vs PUF Panels
Brick and Mortar vs PUF Panels
When starting a construction project, the choice of building materials can significantly impact not only the immediate costs and logistics but also the long-term sustainability and efficiency of the building. This blog explores the Brick and Mortar Construction versus PUF Panels, two popular options that offer distinct advantages and challenges.
Brick and mortar construction has stood the test of time, renowned for its durability and the aesthetic warmth it brings to buildings. This traditional method involves layering bricks with mortar, creating structures that can last for centuries with proper maintenance. It’s a testament to classic building techniques, favored in projects where longevity and classic appeal are paramount.
In contrast, PUF Panels (Polyurethane Foam Panels) represent modern engineering’s answer to demands for Energy-Efficient Building Materials and faster construction times. These panels are celebrated for their excellent insulation properties and lightweight, making them a go-to for Cost-Effective Building Solutions in commercial and residential projects that require quick turnarounds and long-term energy savings.
Choosing the right materials involves a detailed Building Materials Comparison to assess not just upfront costs but also the long-term implications on energy usage, maintenance, and even the building’s environmental impact. Key factors such as Cost, Durability, Energy Efficiency, and Installation Time play critical roles in this decision-making process.
For construction projects, the implications of choosing between Brick and Mortar and PUF Panels can be far-reaching. While brick and mortar offer a timeless look and solid resilience, PUF panels provide a modern, Sustainable Construction Material alternative that aligns with the growing emphasis on green building practices and energy conservation. Each material comes with its own set of advantages, challenges, and suitability depending on the project requirements, making it essential to weigh these factors carefully to align with both practical needs and environmental responsibilities.
As we delve deeper into each material’s properties, costs, and suitable applications, this comparison aims to equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision tailored to your specific construction needs.
What are Brick and Mortar?
Brick and Mortar Construction is one of the oldest and most traditional building methods known to mankind. This technique, which involves layering bricks and binding them together using mortar, has been a cornerstone in building structures that stand the test of time. Its historical use stretches back to ancient civilizations, where it was employed to construct everything from humble homes to vast palaces and fortifications.
Definition and Historical Use
Bricks, typically made from fired clay or cement, combined with mortar—a mixture of water, sand, and cement—are used to create sturdy, load-bearing walls. This method's historical significance is evident in many of the world's oldest surviving buildings, which showcase the durability and strength of Brick and Mortar Construction. From the Roman Colosseum to medieval castles, brick and mortar have been essential in shaping human habitats.
Key Characteristics and Benefits
1) One of the key characteristics of brick and mortar is its incredible durability. Structures built with these materials can withstand harsh weather conditions, fires, and the ravages of time, making them a preferred choice for permanent structures.
2) Additionally, brick walls offer excellent natural insulation, maintaining interior temperatures and contributing to Energy-Efficient Building Materials. Their thermal mass helps cool interiors in summer and retain warmth in winter, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling.
3) Bricks also offer flexibility in design with a variety of colors, textures, and sizes. This allows architects and builders to implement diverse aesthetic and structural designs, making brick a versatile choice for both traditional and contemporary constructions.
4) Moreover, the use of brick and mortar is often considered a Sustainable Construction Material because bricks can be made from natural, abundant materials and are recyclable.
Common Applications and Examples in Modern Construction
Today, Brick and Mortar Construction is not just used for its aesthetic appeal and historical significance but also for its practical benefits in modern construction.
1) It is commonly seen in residential housing, schools, libraries, and other buildings where longevity and minimal maintenance are desirable.
2) Furthermore, many modern commercial projects integrate brick accents or full brick facades to capitalize on its classic visual appeal and structural integrity.
3) Modern examples include innovative architectural designs like the Tate Modern in London or the brick-dominated facades of the new extension of the Royal Danish Library. These structures highlight how traditional materials can be incorporated into modern designs, proving that Brick and Mortar remain critical components in Building Materials Comparison and Cost-Effective Building Solutions.
By leveraging the historical strengths and adapting to new technologies, brick and mortar continue to serve as foundational materials in construction, marrying the past with the future in the ever-evolving landscape of architecture and building.
What are PUF Panels?
PUF Panels, or Polyurethane Foam Panels, represent a cutting-edge solution in the construction industry, particularly noted for their role as Energy-Efficient Building Materials. These panels consist of a rigid core of polyurethane foam, sandwiched between two structural facings. This design not only makes them incredibly lightweight but also exceptionally good at insulating properties.
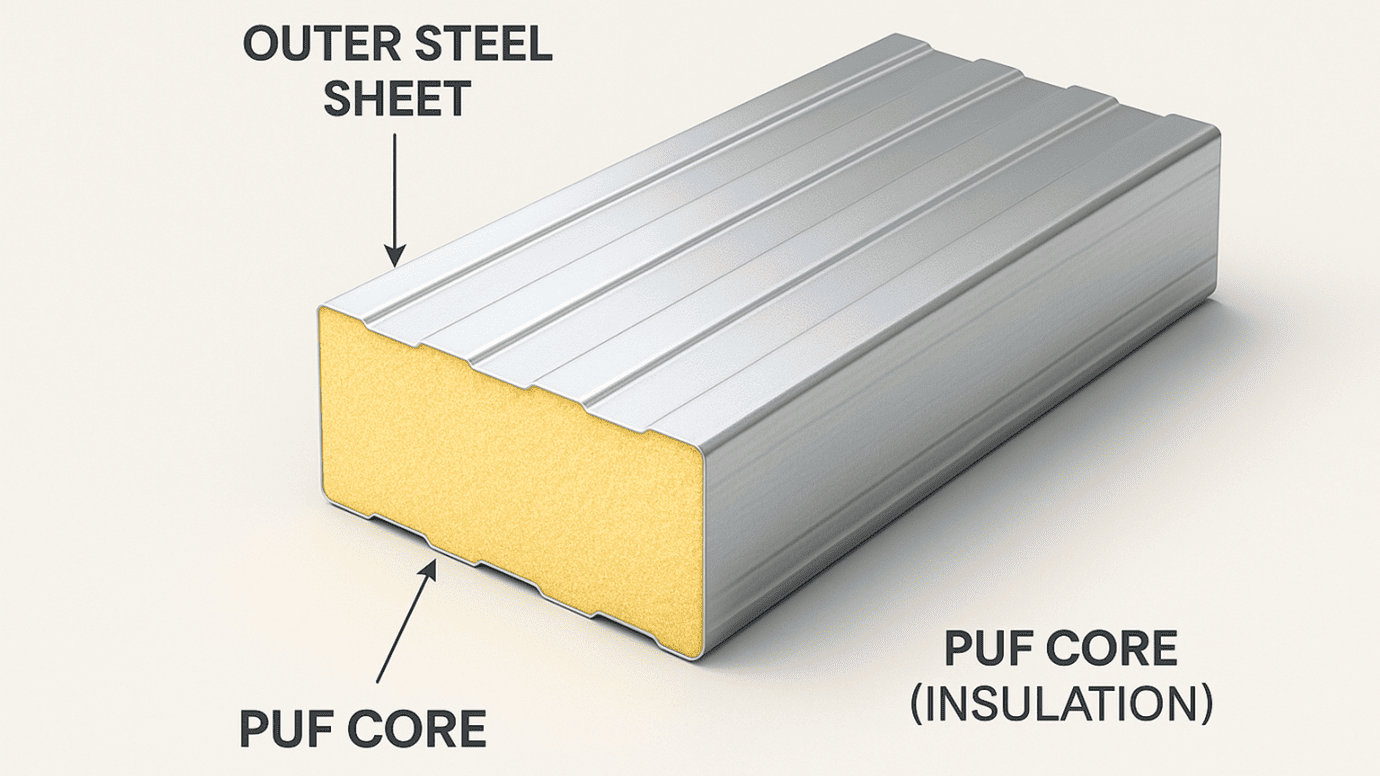
Explanation of Polyurethane Foam Panels and Their Composition
Polyurethane foam, the core material in PUF Panels, is synthesized by reacting a polyol (an alcohol with more than two reactive hydroxyl groups per molecule) with a diisocyanate, in the presence of a blowing agent. This chemical reaction creates a foam that expands and then sets into a solid, dense cellular structure. The outer layers can be made from a variety of materials including steel, aluminum, or fiberglass, providing structural stability and additional protective properties.
Advantages of PUF Panels in Construction
PUF Panels offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice in modern construction scenarios:
- Superior Insulation: The foam core provides outstanding thermal insulation, greatly reducing heating and cooling costs in buildings and contributing to their status as Cost-Effective Building Solutions.
- Lightweight: Their light nature makes PUF panels easy to transport and quick to install, reducing construction times and labor costs.
- Structural Integrity: Despite their light weight, PUF panels are remarkably strong and provide good structural support to buildings.
- Versatility: They can be used in a variety of building designs and applications, adapting easily to different architectural styles.
- Environmental Impact: As a Sustainable Construction Material, PUF panel helps to reduce the overall energy consumption of buildings and are often made from materials that are recyclable.
Typical Uses of PUF Panels in Commercial and Residential Buildings
In the world of construction, PUF Panels are incredibly versatile and find applications across both commercial and residential projects:
- Commercial Buildings: They are commonly used in the construction of warehouses, factories, and cold storages where insulation is crucial for operational efficiency.
- Residential Projects: PUF panels are utilized in homes for roofing and wall panels, particularly in areas that experience extreme weather conditions, thus ensuring better control over indoor climates.
- Prefabricated Constructions: Ideal for prefabricated or modular homes, where quick assembly and energy efficiency are highly valued.
- Clean Rooms and Controlled Environments: Their excellent insulation and airtightness make them suitable for building pharmaceutical labs, hospitals, and other controlled environment facilities.
- Portable Buildings: Often used in the construction of portable or temporary buildings due to their easy installation and lightweight nature.
PUF Panels serve as a cornerstone for Energy-Efficient Building Materials in modern construction, aligning with the needs for Cost-Effective Building Solutions and Sustainable Construction Materials. Whether it’s enhancing energy conservation or streamlining construction processes, PUF panels provide a reliable and innovative building solution that meets the evolving demands of the industry.
Comparing Cost and Installation: Brick and Mortar vs. PUF Panels
When selecting construction materials, a critical aspect to consider is the financial implications—not only the initial investment but also the long-term maintenance and operational costs. Brick and Mortar Construction and PUF Panels both present unique cost profiles and installation dynamics, making a detailed Building Materials Comparison essential for decision-makers.
Cost Comparison of Materials
- Brick and Mortar: Typically, the cost of Brick and Mortar Construction includes the price of the bricks themselves and the mortar, along with the labor-intensive installation process. The overall expense can differ significantly depending on the type of brick used, regional labor costs, and the complexity of the construction design. While brick and mortar provide a high degree of durability and thermal mass, the initial setup cost is generally higher than some modern materials.
- PUF Panels: On the other hand, PUF Panels offer a more Cost-Effective Building Solution upfront. The panels are prefabricated, which means they can be quickly installed on-site, reducing both labor hours and associated costs. Although the material cost for PUF panels might be higher per unit than some types of bricks, the total cost of installation tends to be lower due to the speed and ease of assembly.
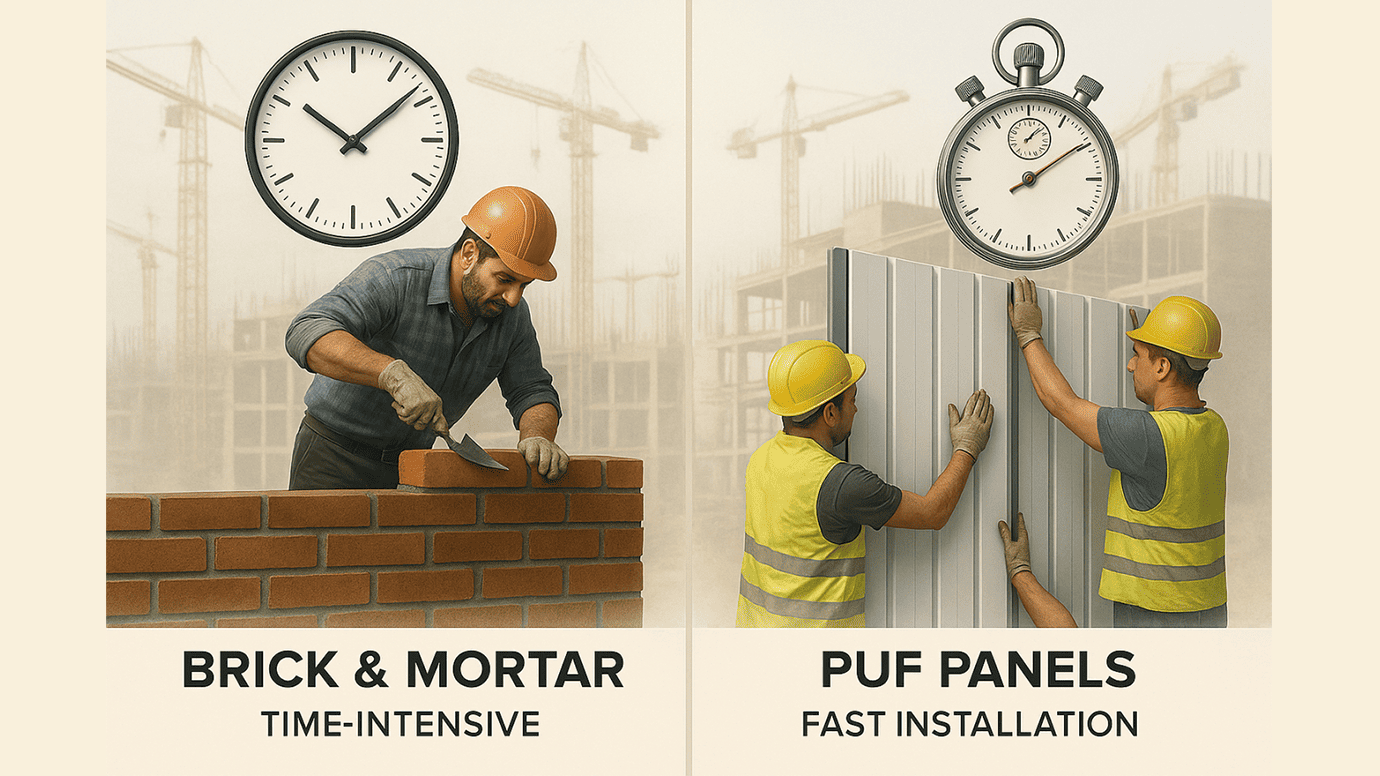
Analysis of Installation Times and Complexity
- Brick and Mortar Construction demands a considerable amount of skill and time, as it involves manual layering of bricks and curing time for mortar. This process can be slow and is subject to weather conditions, which can delay projects further.
- In contrast, PUF Panels are designed for swift assembly. These panels are manufactured in controlled environments and simply need to be positioned and secured on-site, drastically cutting down installation time. The simplicity and speed of installing PUF panels make them particularly attractive for projects with tight deadlines or where labor costs are particularly high.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness and Maintenance
- While Brick and Mortar buildings are esteemed for their longevity and minimal maintenance needs, they might require occasional repointing of mortar and cleaning to maintain their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. However, their robust nature means that these costs are often spread out over many years.
- PUF Panels, meanwhile, boast excellent insulation properties that can lead to substantial savings on energy bills, underscoring their reputation as Energy-Efficient Building Materials. They are also resistant to many of the environmental factors that can degrade other materials, such as moisture and pests, which minimizes repair and maintenance expenses over time. However, they may be susceptible to physical damage and could require more frequent cosmetic repairs than more resilient materials like brick.
The choice between Brick and Mortar and PUF Panels involves a careful evaluation of upfront costs, installation complexities, and long-term financial benefits. While Brick and Mortar remains a tried-and-true option for those valuing tradition and permanence, PUF Panels offer a modern, efficient, and often more Sustainable Construction Material alternative that aligns well with contemporary needs for cost efficiency and environmental responsibility. Each material brings distinct advantages and limitations to the table, making it crucial for builders and developers to align their material choices with their specific project requirements and long-term goals.
Durability and Maintenance: A Key Factor in Building Materials Comparison
When evaluating construction materials for any project, assessing the durability and maintenance requirements of those materials is crucial. Not only do these factors impact the longevity and aesthetics of a building, but they also influence the overall cost-effectiveness and sustainability of the construction. In this section, we compare Brick and Mortar Construction with PUF Panels regarding their durability, resistance to environmental factors, and ongoing maintenance needs.
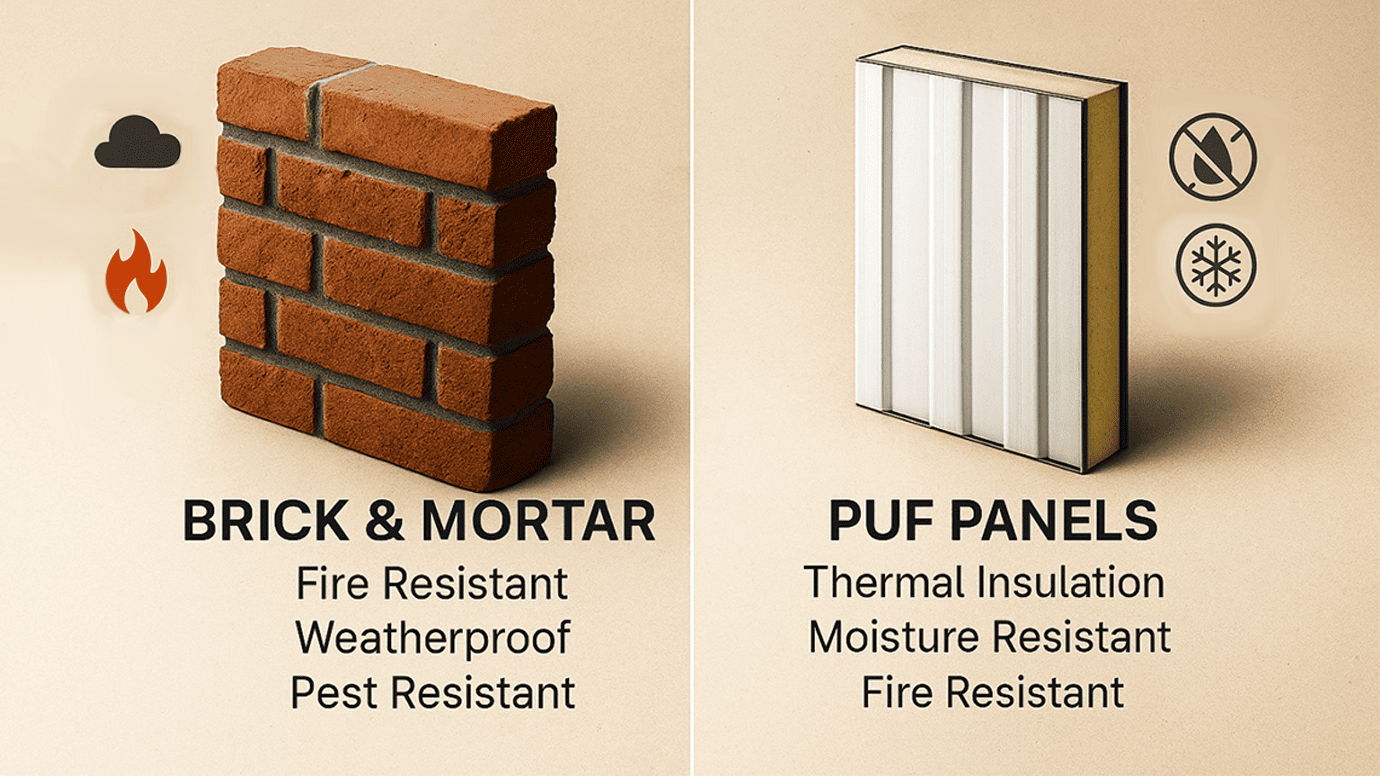
Durability and Longevity of Brick and Mortar
Brick and Mortar Construction is synonymous with durability and strength. This traditional building method, where layers of bricks are bonded together with mortar, creates structures that can last for centuries. Historical buildings made from brick and mortar that are still standing today are testament to the material’s longevity. Bricks are inherently resistant to fire, pests, and rot, which contributes significantly to their durability. However, the mortar may require periodic maintenance to prevent water ingress and to ensure structural integrity.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors: Brick and mortar are highly resistant to harsh weather conditions, including high winds and heavy rains, which makes them an excellent choice for regions prone to such climates.
- Maintenance Needs: While brick structures are durable, the mortar joints may erode over time and require repointing to ensure water resistance and structural stability. Regular cleaning may also be necessary to prevent moss and mildew growth, especially in damp climates.
Durability and Resistance of PUF Panels
PUF Panels, known for their role as Energy-Efficient Building Materials, also offer considerable durability. These panels consist of polyurethane foam sandwiched between protective layers, which can be tailored to resist various environmental factors.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors: PUF panels are excellent insulators and are generally resistant to moisture, which prevents the common problems of mold and rot. Additionally, when properly treated, these panels can also be made fire resistant and capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, both hot and cold.
- Maintenance Needs: One of the advantages of PUF panels is their low maintenance requirement. They do not need frequent upkeep beyond occasional cleaning to maintain their appearance and functionality. However, they can be susceptible to physical impact damage, requiring prompt repair to maintain their insulative properties and structural integrity.
Impact on Overall Cost and Usability
- Brick and Mortar: The initial cost of building with brick might be higher due to material costs and labor-intensive installation. However, the minimal maintenance required over a long period can make brick a more Cost-Effective Building Solution in the long term. The durability of brick and mortar construction also adds to the property’s value, making it a Sustainable Construction Material in terms of economic sustainability.
- PUF Panels: While the upfront cost of PUF panels can be lower, especially when factoring in the rapid installation and reduced labor costs, potential expenses can arise from the need to repair or replace panels damaged by impacts or harsh environmental conditions. Nonetheless, the superior insulation properties of PUF panels can lead to great savings on energy costs, bolstering their reputation as Cost-Effective Building Solutions and Sustainable Construction Materials.
Both Brick and Mortar Construction and PUF Panels offer unique advantages in terms of durability and maintenance. The choice between these materials should consider the specific environmental conditions and the expected longevity of the structure, alongside the financial implications associated with initial construction, ongoing upkeep, and potential energy savings.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact: Assessing Brick and Mortar vs. PUF Panels
In the context of modern construction, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact are increasingly critical considerations. The choice between traditional Brick and Mortar Construction and modern PUF Panels must account for both thermal insulation properties and the broader environmental implications of production, usage, and disposal.
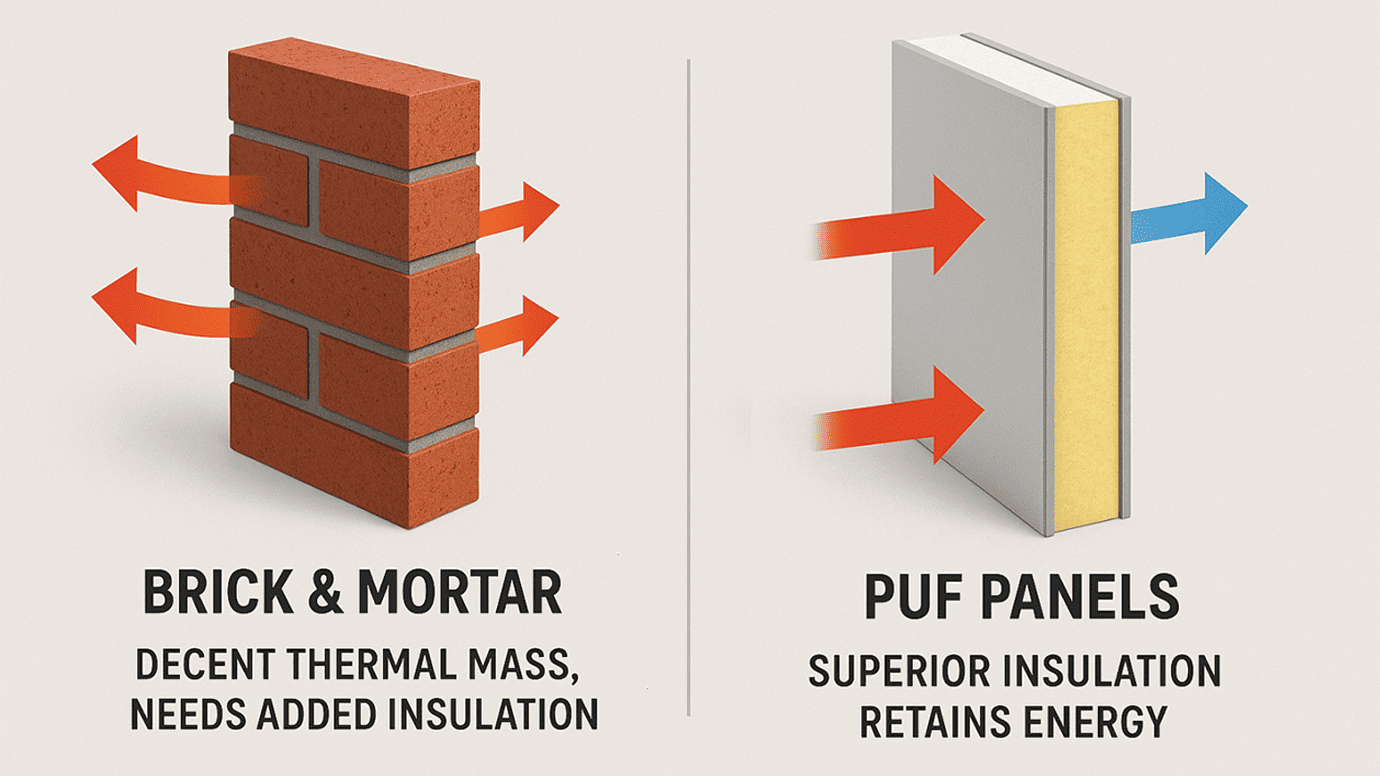
Thermal Insulation Properties
- Brick and Mortar: While traditional brick walls have decent thermal mass, which helps stabilize indoor temperatures by absorbing and slowly releasing heat, they are not inherently great insulators without additional materials. To achieve better Energy Efficiency, brick constructions often require added insulation layers, which can complicate construction and increase costs.
- PUF Panels: Designed specifically with Energy Efficiency in mind, PUF Panels excel in insulation. The core of polyurethane foam provides superior thermal resistance, significantly reducing the need for external heating and cooling. This attribute makes PUF panels a staple in Energy-Efficient Building Materials, particularly suitable for climates with extreme temperature variations.
Environmental Impact of Production and Disposal
- Brick and Mortar:
- Production: The production of bricks involves high-temperature kilning, usually fueled by natural gas or coal, which can contribute to significant CO2 emissions. However, innovations such as the introduction of kilns using cleaner energy sources and recycled materials are helping to reduce this impact.
- Disposal: Brick and mortar are largely inert materials that do not emit harmful substances upon disposal. Moreover, bricks can often be recycled or reused in other projects, enhancing their credentials as Sustainable Construction Materials.
- PUF Panels:
- Production: Manufacturing PUF panels involves chemical processes that can be energy-intensive and involve potentially hazardous materials. However, the industry is moving towards more environmentally friendly blowing agents and production methods.
- Disposal: The disposal of PUF panels can be problematic, as they are not as easily recyclable as bricks. Specialized processes are required to break down and recycle these panels, although advances are being made in this area as well.
Alignment with Modern Sustainable Building Practices
- Brick and Mortar: The longevity and durability of brick constructions contribute to their sustainability by minimizing the frequency of rebuilds or major repairs. Additionally, the push towards using recycled materials in brick production and the possibility of reusing bricks make it a Sustainable Building Material under current building practices.
- PUF Panels: Despite some challenges in production and disposal, the energy savings offered by PUF panels during the operational phase of a building align well with sustainable practices. Their light weight reduces transportation emissions, and their exceptional insulation properties decrease the energy required for heating and cooling, affirming their status as Cost-Effective Building Solutions.
When evaluating Brick and Mortar Construction and PUF Panels through the lens of energy efficiency and environmental impact, it’s clear that both materials have their merits and drawbacks. The choice between them should consider specific project needs, environmental priorities, and the overall sustainability strategy of the construction project. Both materials offer pathways to integrate with modern Sustainable Construction Materials, albeit in different ways, highlighting the significance of tailored solutions in the pursuit of building greener, more sustainable buildings.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility: Brick and Mortar vs. PUF Panels
The aesthetic appeal and design flexibility of construction materials not only influence the architectural character of a building but also play a crucial role in how a structure integrates with its environment and meets the functional needs of its inhabitants. When comparing Brick and Mortar Construction with PUF Panels, it’s important to consider how each material influences design aesthetics and architectural possibilities.
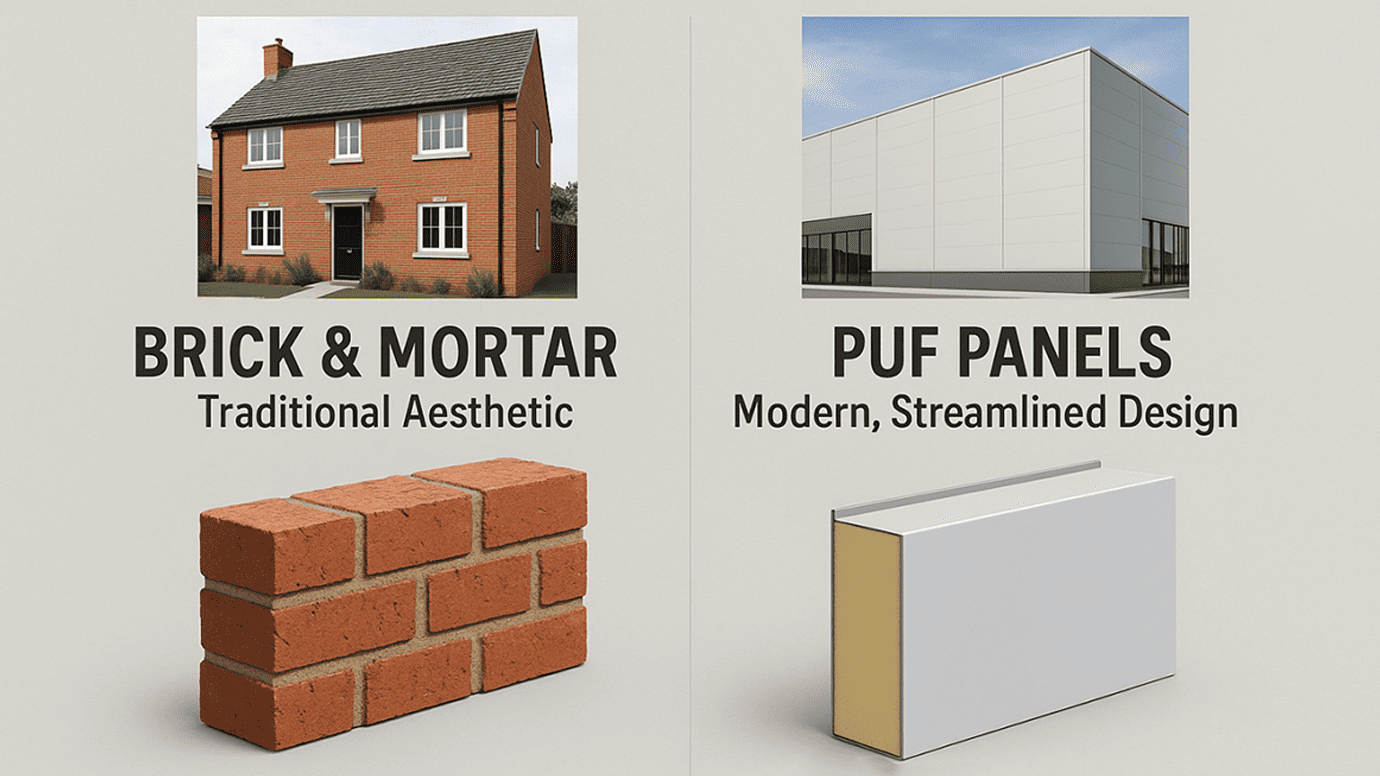
Aesthetic Differences
- Brick and Mortar Construction: Bricks have a timeless appeal that can convey both traditional and contemporary aesthetics depending on the type of brick and the method of application. With a variety of colors, textures, and sizes available, brick provides architects and designers with a strong palette to create visually impactful designs. Whether it’s the classic red brick or the more modern glazed varieties, brick can enhance the exterior and interior of buildings with its rich, natural textures and color depth.
- PUF Panels: While PUF Panels might lack the natural aesthetic variety of brick, they offer a sleek, modern look that can be very appealing in contemporary commercial and industrial designs. They are typically finished with a range of coatings and facings, such as metal or plastic composites, which can be customized in an array of colors and finishes to suit a number of architectural styles. This makes PUF panels versatile for modern constructions where efficiency and a clean, streamlined appearance are desired.
Impact on Architectural Design
- Brick and Mortar Construction: The versatility of brick allows it to be used in a myriad of architectural styles, from historic renovations to modern residential homes. Bricks can be laid in various patterns to create unique textural and dimensional effects. Their robustness and ease of integration with other materials make brick a popular choice for architects who wish to blend durability with classic aesthetics.
- PUF Panels: The lightweight nature of PUF Panels significantly affects architectural design, especially in projects requiring quick assembly and reduced structural loads. Their ease of installation and ability to cover large areas quickly make them ideal for expansive commercial spaces. Additionally, their insulative properties can be maximally utilized in designs focusing on energy efficiency.
Limitations and Creative Uses
- Brick and Mortar Construction: While brick provides substantial durability and aesthetic flexibility, it does have limitations, especially in terms of structural load and insulation capabilities without additional materials. However, creative uses of brick such as curved walls, intricate laying patterns, and mixed-material facades have allowed architects to push the boundaries of traditional brick construction.
- PUF Panels: One limitation of PUF panels is their vulnerability to physical impacts and harsh environmental conditions, which may require additional protective layers. Creatively, PUF panels are being used in modular and prefabricated buildings, and their lightweight and easy-to-cut nature allows for rapid construction and bold, modern architectural forms that are both cost-effective and sustainable.
In summary, brick and mortar construction and PUF Panels each offer unique advantages in terms of aesthetic appeal and design flexibility. While brick excels in natural beauty and traditional designs, PUF panels offer a modern, customizable solution ideal for efficient, contemporary building practices. Each material’s properties should be carefully considered in the context of their intended use, ensuring that both functional and aesthetic criteria are met in innovative and sustainable ways.
FAQs:
Q. What is brick and mortar construction?
- Brick and mortar construction involves using bricks as the building blocks and mortar to bind them together, offering a traditional aesthetic and considerable durability.
Q. How do PUF panels enhance energy efficiency in buildings?
- PUF panels provide superior thermal insulation, reducing the need for extra heating and cooling in buildings, which makes them an energy-efficient building material.
Q. Can PUF panels be considered sustainable construction materials?
- Yes, PUF panels are considered sustainable due to their energy efficiency and the reduced environmental impact during their use phase, despite concerns about their production and disposal.
Q. What are the typical applications of PUF panels in construction?
- PUF panels are typically used in commercial buildings, prefabricated structures, and residential projects where quick installation and excellent insulation are priorities.
Q. Why is brick and mortar preferred for traditional construction projects?
- Brick and mortar is preferred for its timeless appearance, robustness, and the cultural value it adds, making it ideal for projects where aesthetics and tradition are important.
Q. What are the environmental impacts of producing brick and mortar?
- The production of brick and mortar can have major environmental impacts due to the energy used in firing bricks and the CO2 emissions from non-renewable energy sources.
Q. How do PUF panels compare to brick and mortar in terms of installation time and cost?
- PUF panels typically require less installation time and are more cost-effective in terms of labor due to their lightweight and prefabricated nature, unlike the labor-intensive process required for brick and mortar construction.
Q. How do both brick and mortar and PUF panels align with modern sustainable building practices?
- Brick and mortar can be sustainable through the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient designs, while PUF panels contribute to sustainability primarily through excellent insulation properties and reduced operational energy consumption.
Q. What design innovations are possible with PUF panels in modern construction?
- Innovations include modular and prefabricated designs that reduce construction time, as well as sleek, modern aesthetics that can be customized for various uses.
Q. Can combining brick and mortar with PUF panels offer a balanced building solution?
- Yes, combining these materials can harness the robustness and aesthetic appeal of brick with the energy efficiency and modernity of PUF panels, delivering a balanced and sustainable construction solution.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ve examined the distinct characteristics and varying advantages of both Brick and Mortar Construction and PUF Panels. Each material has proven its value in different contexts within the construction industry, reflecting unique pros and cons that make them suitable for specific project demands and environmental considerations.
Brick and Mortar Construction is revered for its durability and classic aesthetic appeal. It provides a robust selection of design possibilities that can cater to both traditional and modern architectural styles. However, it tends to involve higher initial costs and longer installation times compared to more modern materials. Periodic maintenance is also necessary to uphold its structural integrity and visual allure.
On the other hand, PUF Panels are celebrated for their exceptional insulation properties and lightweight nature, which allow for rapid construction schedules—ideal for projects under tight timelines. These panels stand out as Cost-Effective Building Solutions, significantly reducing labor costs and enhancing energy efficiency. Yet, they might lack the aesthetic diversity of traditional materials and face challenges in terms of environmental sustainability during production and disposal.
When selecting materials for a construction project, it’s vital to thoroughly assess the specific needs of the building, including its purpose, location, and the importance of environmental sustainability. For projects where aesthetic tradition and long-term durability are crucial, Brick and Mortar may be the better choice. Conversely, PUF Panels should be considered for projects prioritizing quick completion, modern aesthetics, and energy efficiency.
Ultimately, the decision should not be about choosing one material over the other but rather understanding how each can be used to enhance the other’s properties. Integrating both materials into a project can capitalize on the benefits of each—using PUF panels for their insulation capabilities within a brick structure can optimize both energy efficiency and aesthetic value.
By weighing the advantages and limitations of each material in alignment with project-specific goals, builders and developers can make informed decisions that balance cost, design, and sustainability. This approach not only results in the successful completion of construction projects but also supports the development of buildings that are environmentally responsible and suitable for their intended use. Encouraging a blend of both traditional and modern materials may result in structures that are not just functional and attractive but also prepared to meet the challenges of modern building requirements.
